Inpage Navigation Section: Overview
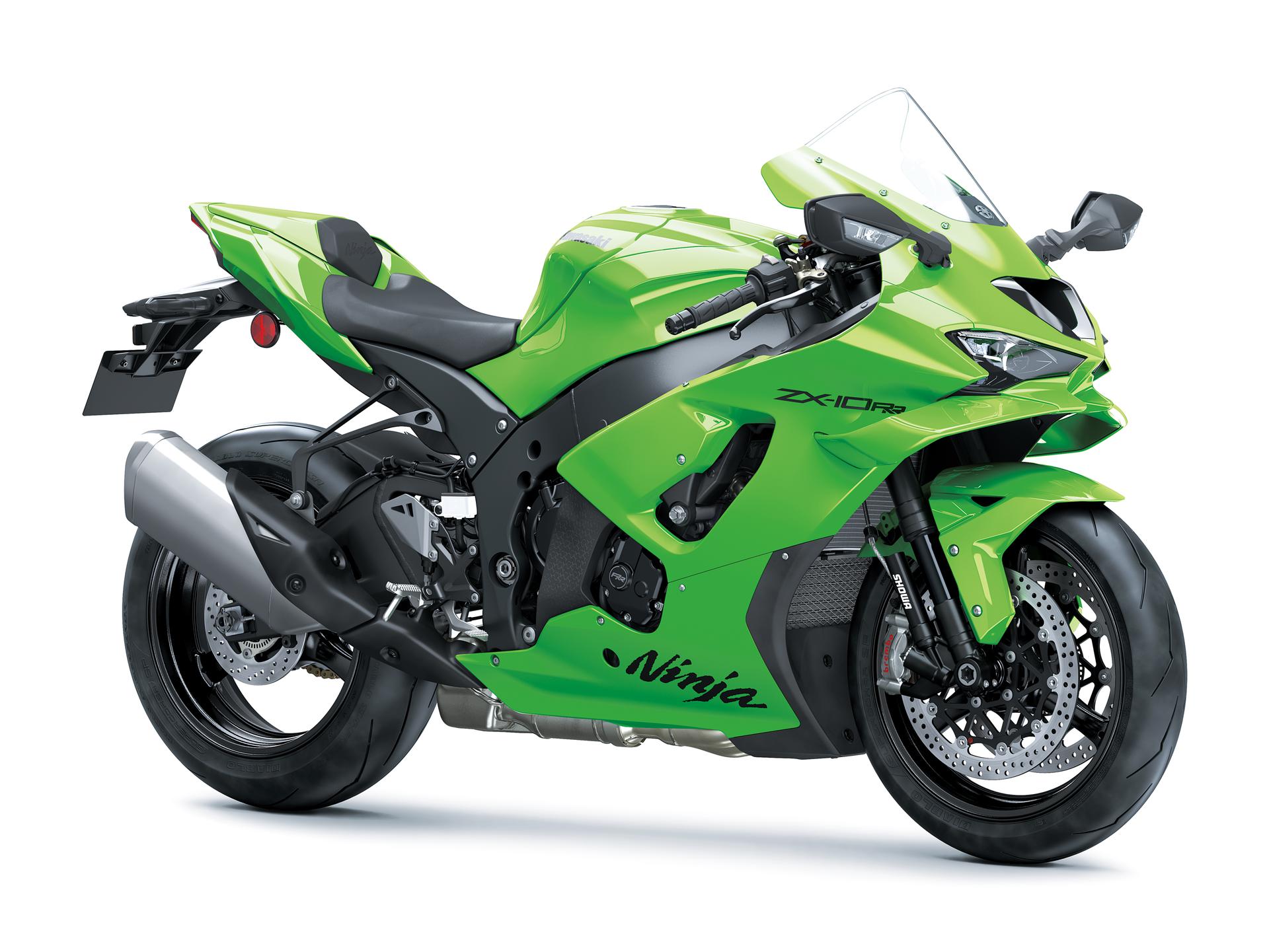
The Ninja ZX-10RR is built for those who rise to a challenge, a true champion Supersport machine.
From carrying Kawasaki riders to 7 WorldSBK Championship titles to helping performance enthusiasts explore their limits on the track, the Ninja ZX-10RR now reaches new heights.
With new aerodynamic winglets and its new sharp, aggressive design, this is the next-generation Ninja.
Push your limits aboard the new Ninja ZX-10RR equipped with a potent 998cc 4-cylinder engine, a fine-tuned chassis and suspension, a state-of-the-art electronics package plus a whole lot more.
Action images show motorcycle prepared for track use (not available for delivery in this form). Road motorcycle includes indicators, rear view mirrors and number plate.
Colour

Show all
Show less

Edition Accessories
Show all
Show less
Inpage Navigation Section: Gallery
Inpage Navigation Section: Features & Specs
High-performance Pankl titanium connecting rods and lightweight Pankl pistons contribute to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s high-revving performance.
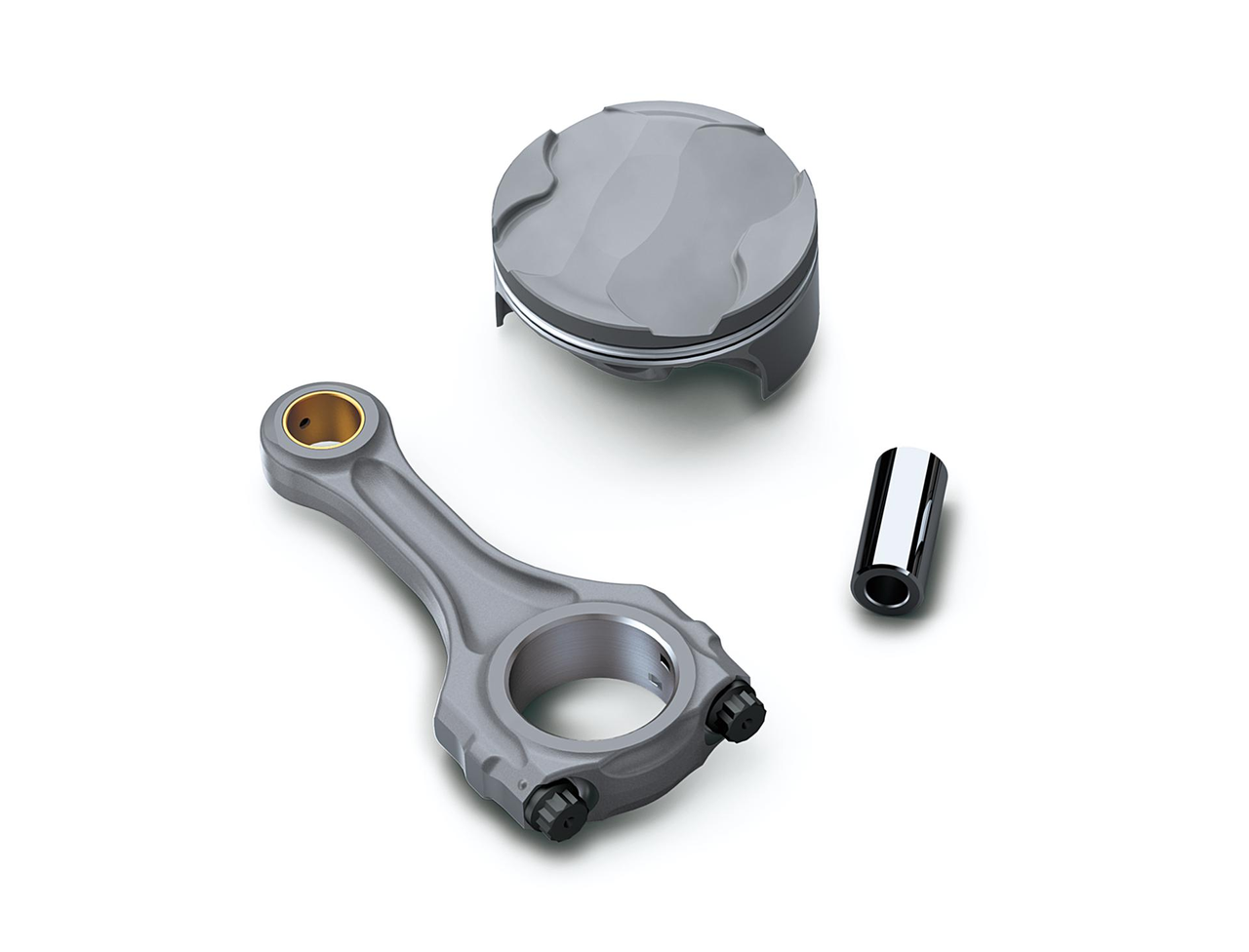

High-performance Pankl titanium connecting rods and lightweight Pankl pistons contribute to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s high-revving performance.
A prime example of form following function, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s latest bodywork was developed with aerodynamic performance as a top priority. The redesigned front cowl features large winglets that significantly increase downforce at high speeds. Combined with updated chassis geometry, the new aerodynamic package enhances high-speed control, cornering performance, and overall circuit potential.

A prime example of form following function, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s latest bodywork was developed with aerodynamic performance as a top priority. The redesigned front cowl features large winglets that significantly increase downforce at high speeds. Combined with updated chassis geometry, the new aerodynamic package enhances high-speed control, cornering performance, and overall circuit potential.
With an engine and chassis designed for chasing lap times on the track, the Ninja ZX-10RR offers a high level of circuit riding potential. To ensure it continues its race-winning ways, Kawasaki engineers fine-tuned the chassis geometry to fully capitalise on the enhanced aerodynamics.
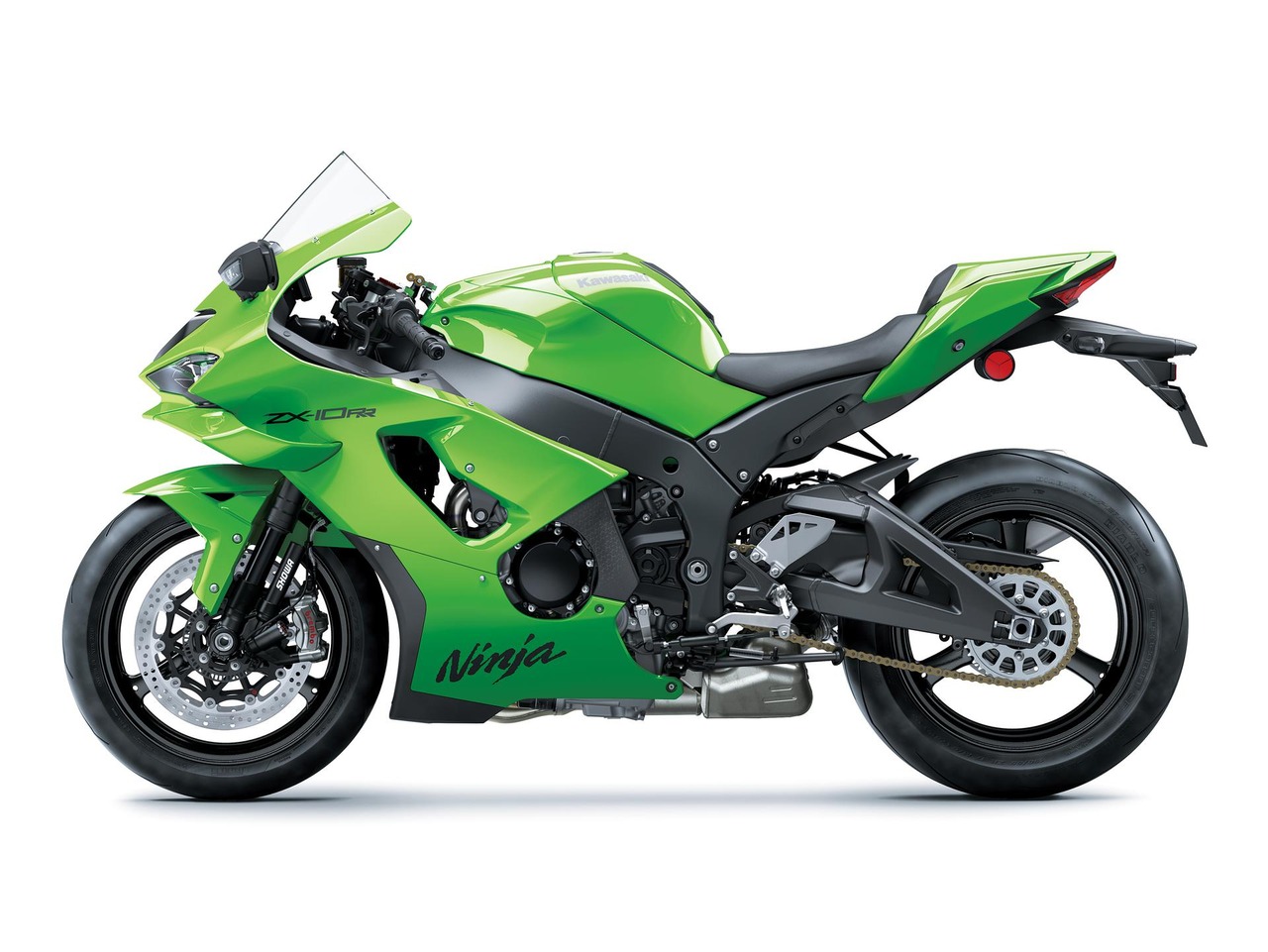

With an engine and chassis designed for chasing lap times on the track, the Ninja ZX-10RR offers a high level of circuit riding potential. To ensure it continues its race-winning ways, Kawasaki engineers fine-tuned the chassis geometry to fully capitalise on the enhanced aerodynamics.
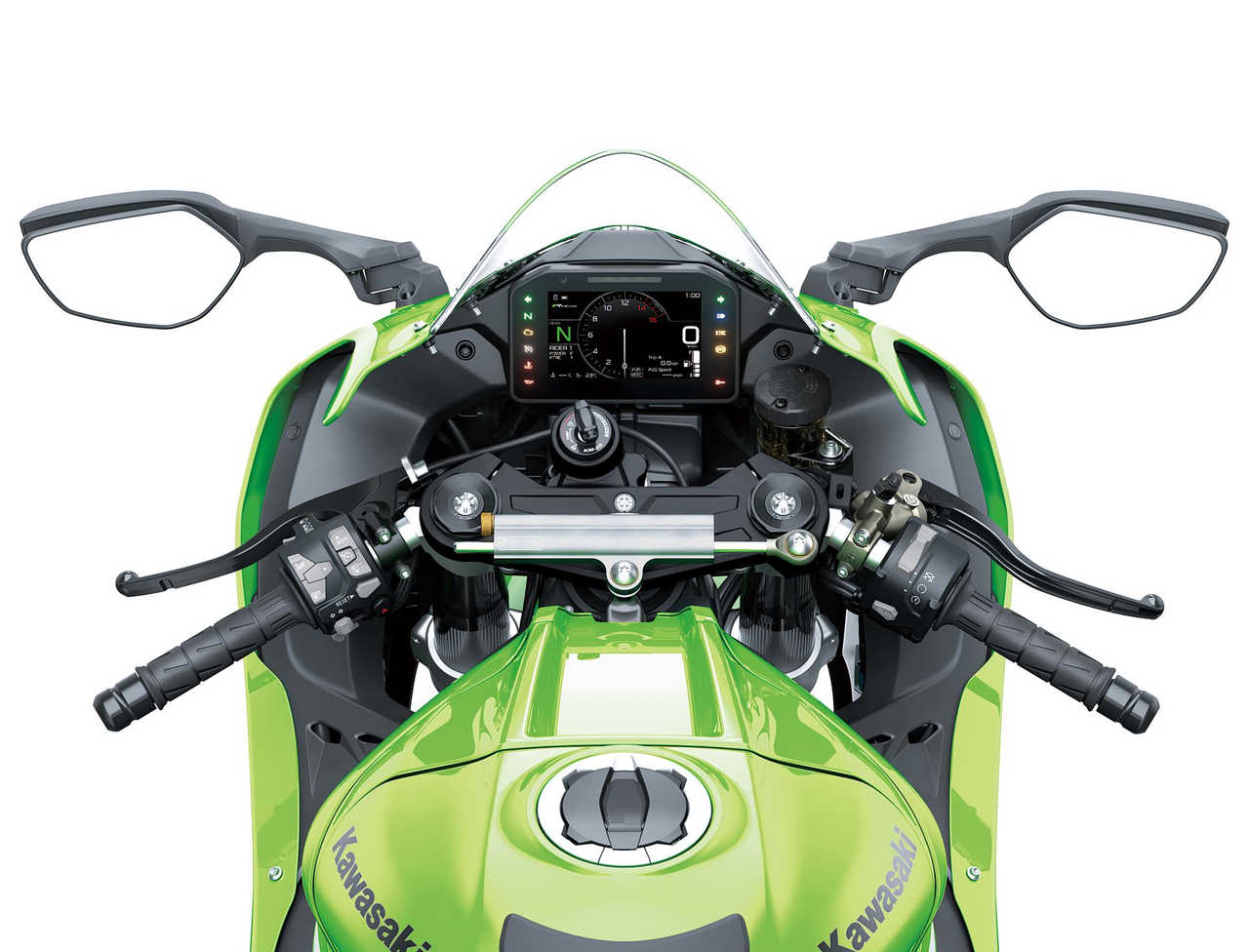
Powered by Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modelling program and enhanced with input from a Bosch IMU, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s cutting-edge electronics enhance the fun of piloting a high-performance supersport machine. Features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, and TFT instrumentation with turn-by-turn navigation capability add convenience and entertainment value, increasing street-riding enjoyment.
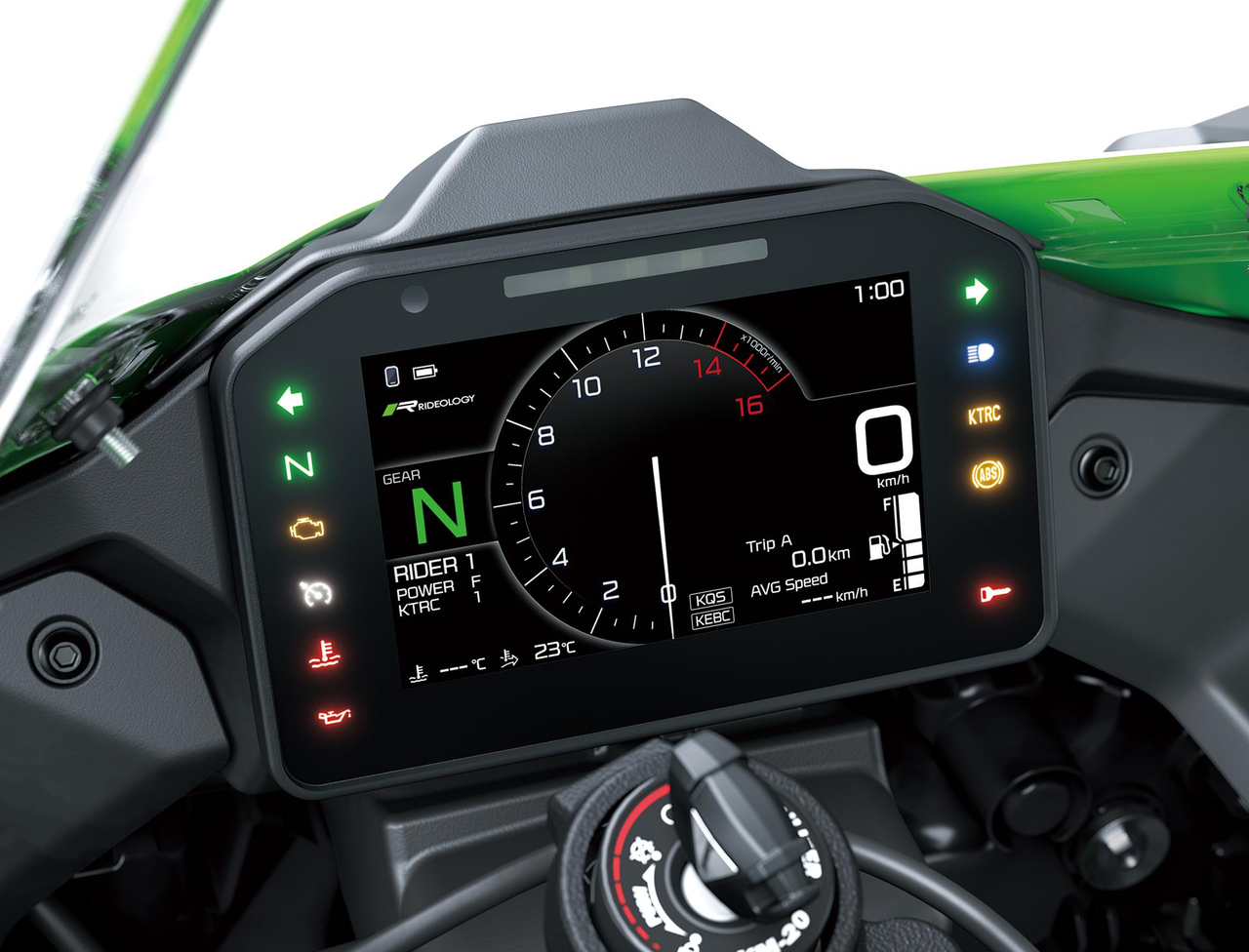

Powered by Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modelling program and enhanced with input from a Bosch IMU, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s cutting-edge electronics enhance the fun of piloting a high-performance supersport machine. Features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, and TFT instrumentation with turn-by-turn navigation capability add convenience and entertainment value, increasing street-riding enjoyment.
Dual high-spec Brembo M50 monobloc calipers gripping large Ø 330 mm discs, specially prepared radial-pump master cylinder and race-quality steel-braided lines deliver next-level braking performance.
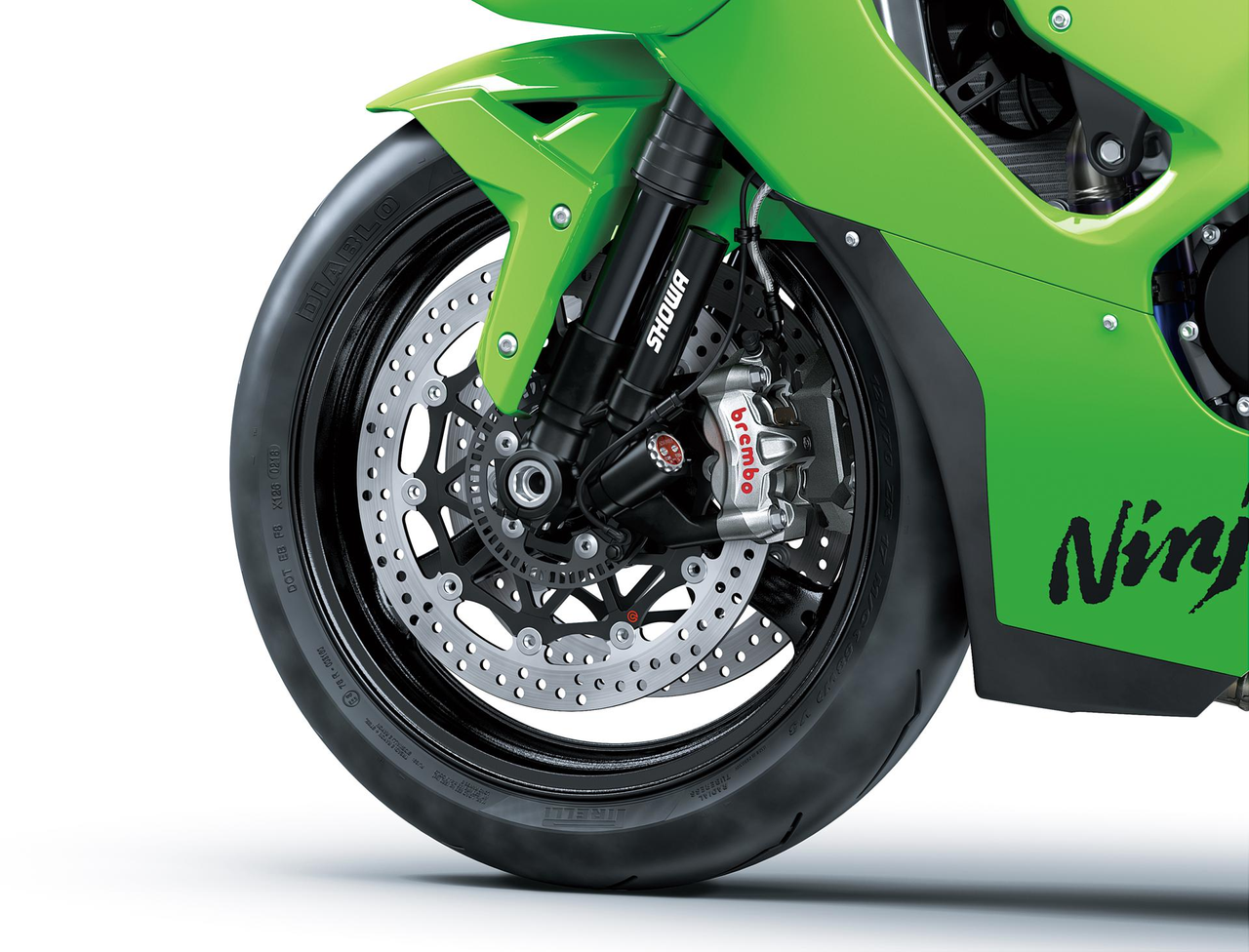

Dual high-spec Brembo M50 monobloc calipers gripping large Ø 330 mm discs, specially prepared radial-pump master cylinder and race-quality steel-braided lines deliver next-level braking performance.
Adding to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s highly acclaimed control, cornering performance, and light handling, updates to the chassis geometry—tuned to match the effect of the new winglets—contribute to improved rear-wheel traction and enhanced secondary cornering force, which facilitates steering the bike from the rear when track riding.
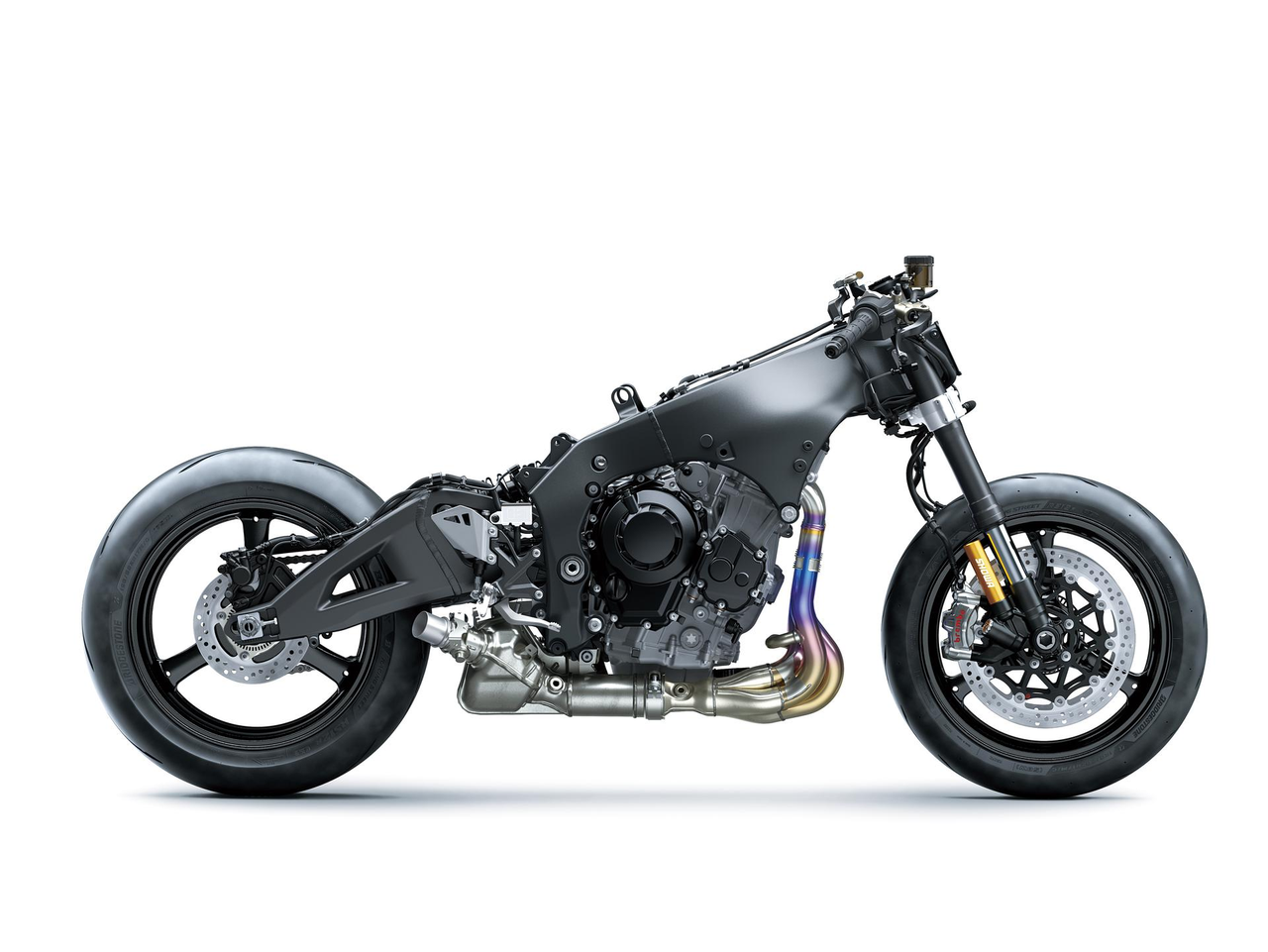

Adding to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s highly acclaimed control, cornering performance, and light handling, updates to the chassis geometry—tuned to match the effect of the new winglets—contribute to improved rear-wheel traction and enhanced secondary cornering force, which facilitates steering the bike from the rear when track riding.
Circuit-focused settings for the WorldSBK-developed BFF (Balance Free Front Fork) and BFRC lite (Balance Free Rear Cushion) shock facilitate front-rear weight transfer and contribute to light handling.
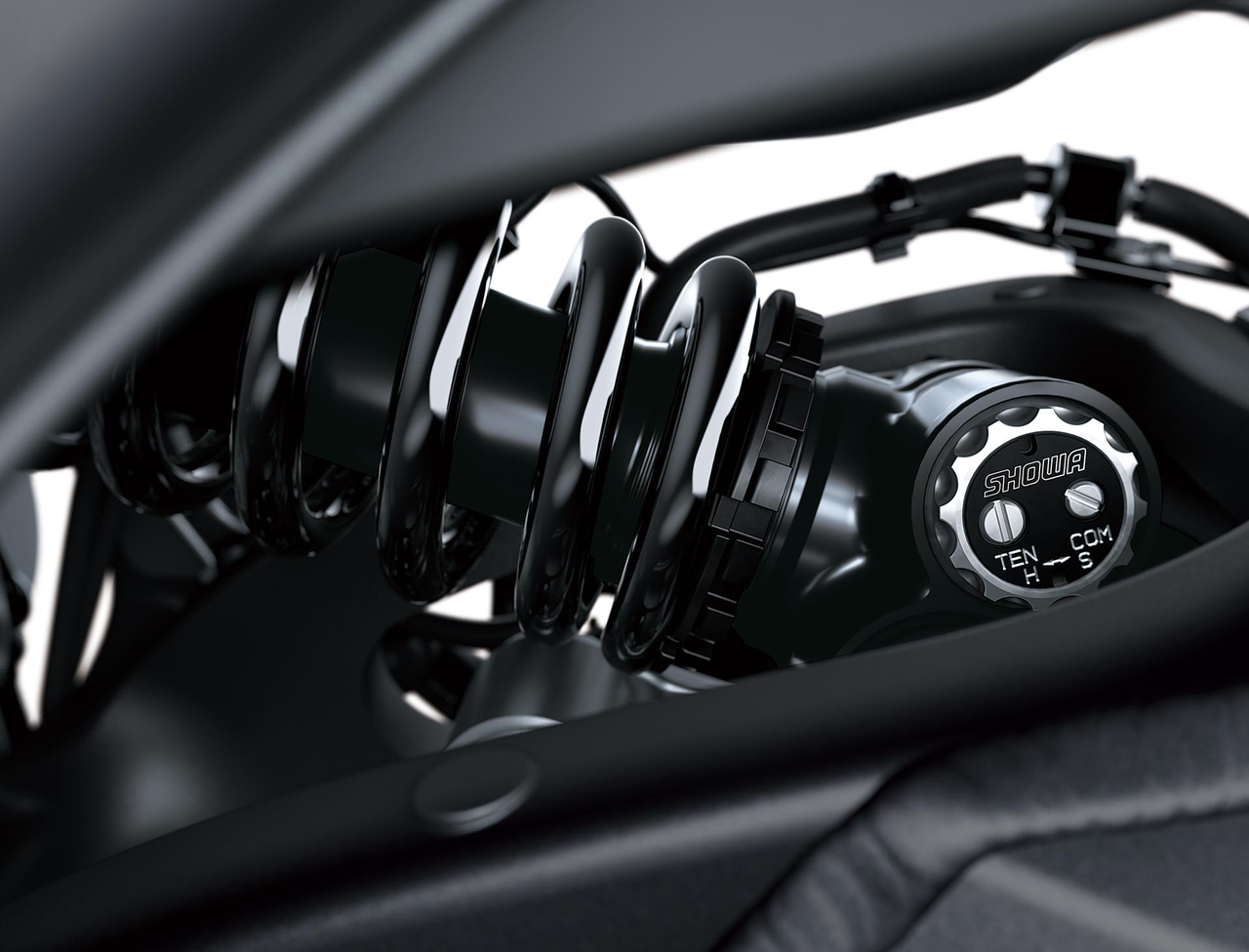

Circuit-focused settings for the WorldSBK-developed BFF (Balance Free Front Fork) and BFRC lite (Balance Free Rear Cushion) shock facilitate front-rear weight transfer and contribute to light handling.
For riders who enjoy street riding, features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, smartphone connectivity, and full-colour TFT instrumentation with a gimbal-style lean angle display and turn-by-turn navigation* offer even greater satisfaction.
*Navigation functions will be available only to users who have a licence.
**Feature availability varies by market.

For riders who enjoy street riding, features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, smartphone connectivity, and full-colour TFT instrumentation with a gimbal-style lean angle display and turn-by-turn navigation* offer even greater satisfaction.
*Navigation functions will be available only to users who have a licence.
**Feature availability varies by market.
Handlebar and footpeg positions contribute to an aggressive, circuit-focused riding position that also helps riders minimise drag when tucked behind the windshield going down the straight.

Handlebar and footpeg positions contribute to an aggressive, circuit-focused riding position that also helps riders minimise drag when tucked behind the windshield going down the straight.
The Ninja ZX-10RR’s engine balances stunning power with manageability, offering linear power delivery right to its heady peak power. For maximum track-riding efficiency, great care was taken to ensure ideal engine manageability during all parts of the corner: getting off the throttle in corner entry, getting back on the throttle mid-corner, opening the throttle on corner exit. The new engine maintains the high performance of its predecessor while offering improved emissions.
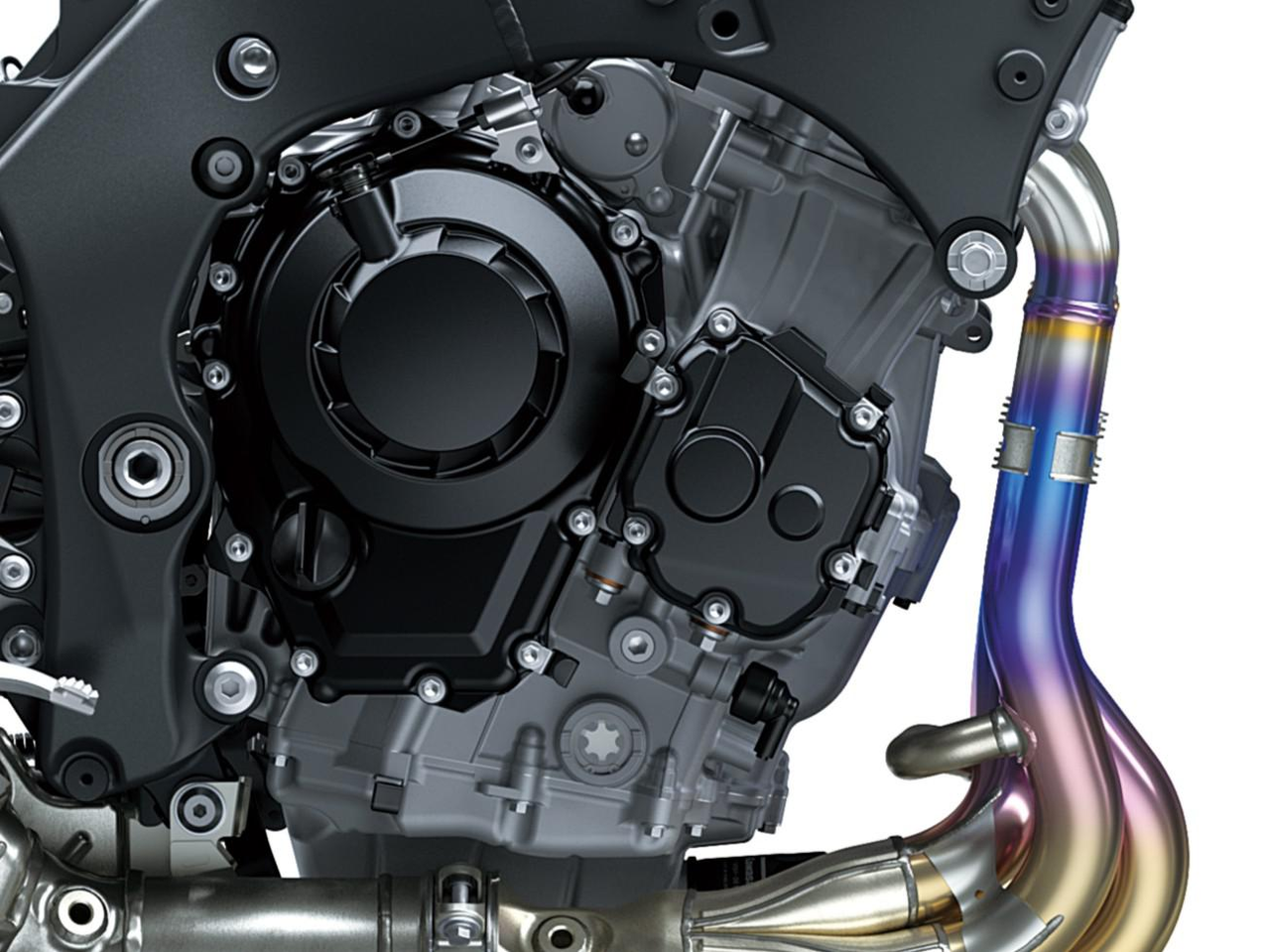
The Ninja ZX-10RR’s engine balances stunning power with manageability, offering linear power delivery right to its heady peak power. For maximum track-riding efficiency, great care was taken to ensure ideal engine manageability during all parts of the corner: getting off the throttle in corner entry, getting back on the throttle mid-corner, opening the throttle on corner exit. The new engine maintains the high performance of its predecessor while offering improved emissions.
Compact projector/reflector hybrid headlights, repositioned Ram Air intake and prominent new winglets give the Ninja ZX-10RR its new “face,” enhancing the strong Ninja family image. All-new sharp, aggressive bodywork creates a dynamic image that completes the next-generation Ninja styling.
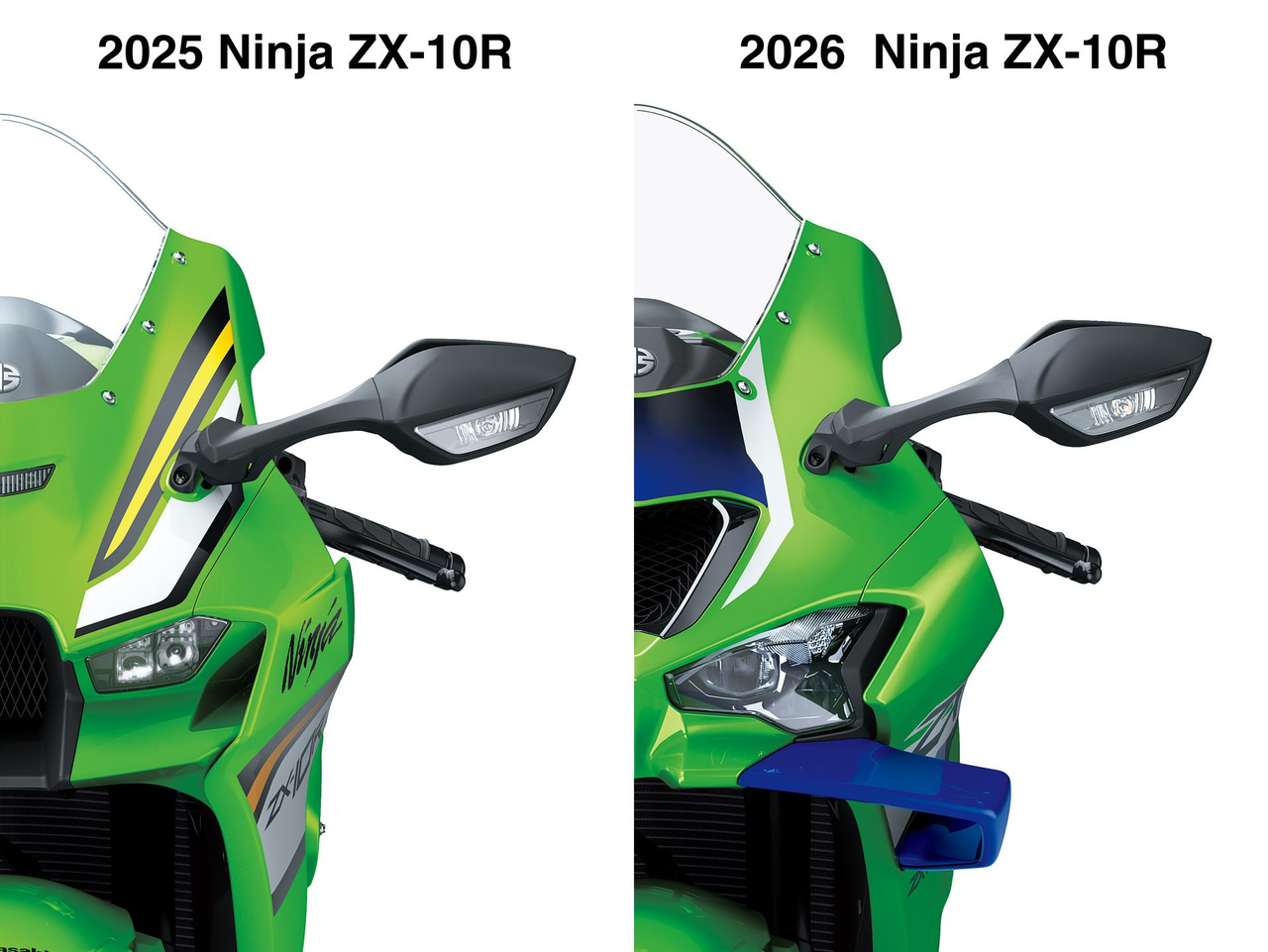

Compact projector/reflector hybrid headlights, repositioned Ram Air intake and prominent new winglets give the Ninja ZX-10RR its new “face,” enhancing the strong Ninja family image. All-new sharp, aggressive bodywork creates a dynamic image that completes the next-generation Ninja styling.
The winglets extending to either side not only highlight the machine’s advanced aerodynamic performance, but also effectively generate downforce that increases front-end feel for greater cornering confidence.
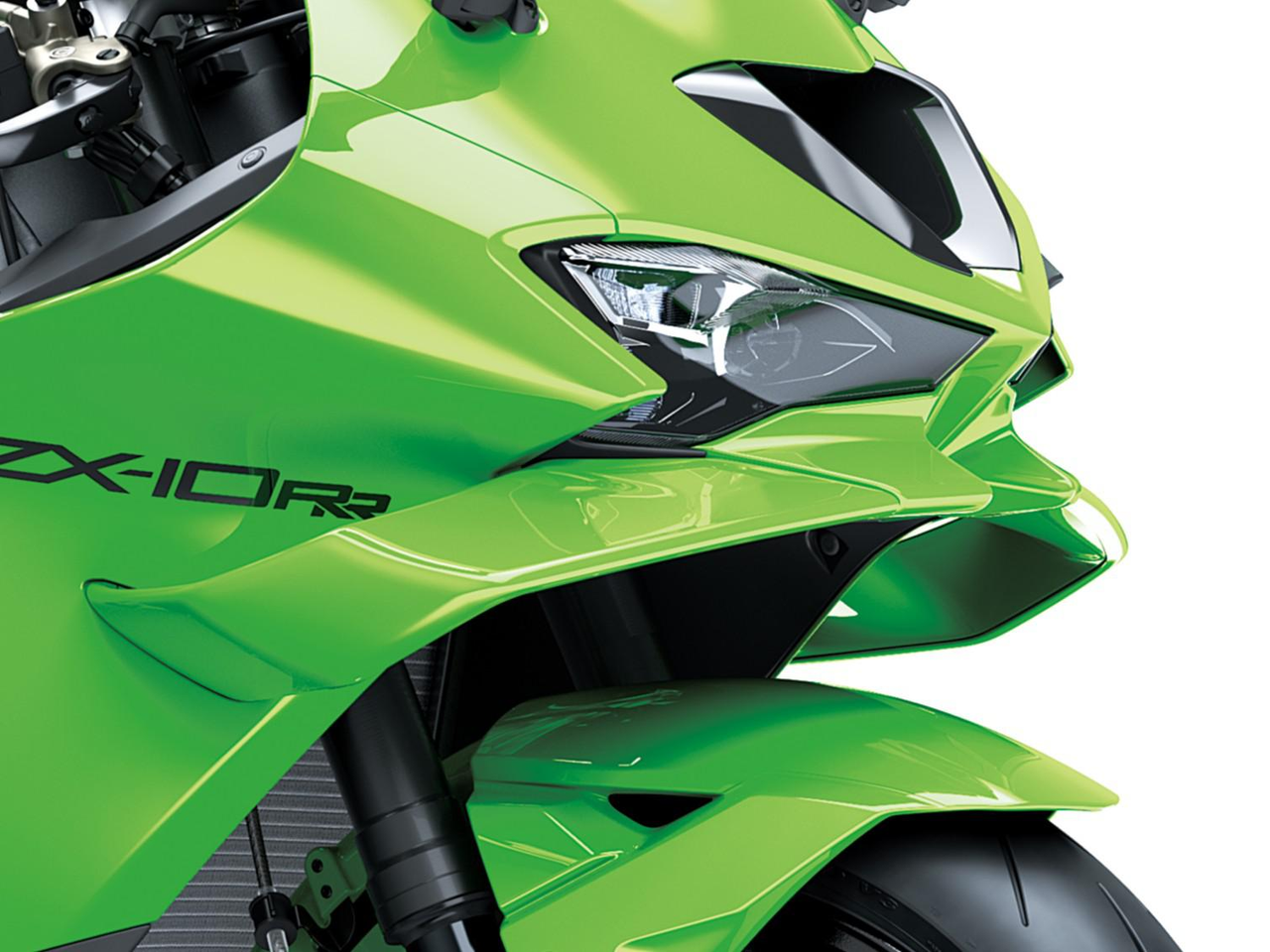

The winglets extending to either side not only highlight the machine’s advanced aerodynamic performance, but also effectively generate downforce that increases front-end feel for greater cornering confidence.
The highly sophisticated electronic management systems on the Ninja ZX-10RR facilitate rider control and allow riders to experience what it is like to ride a high-powered superbike at the limit on the track.
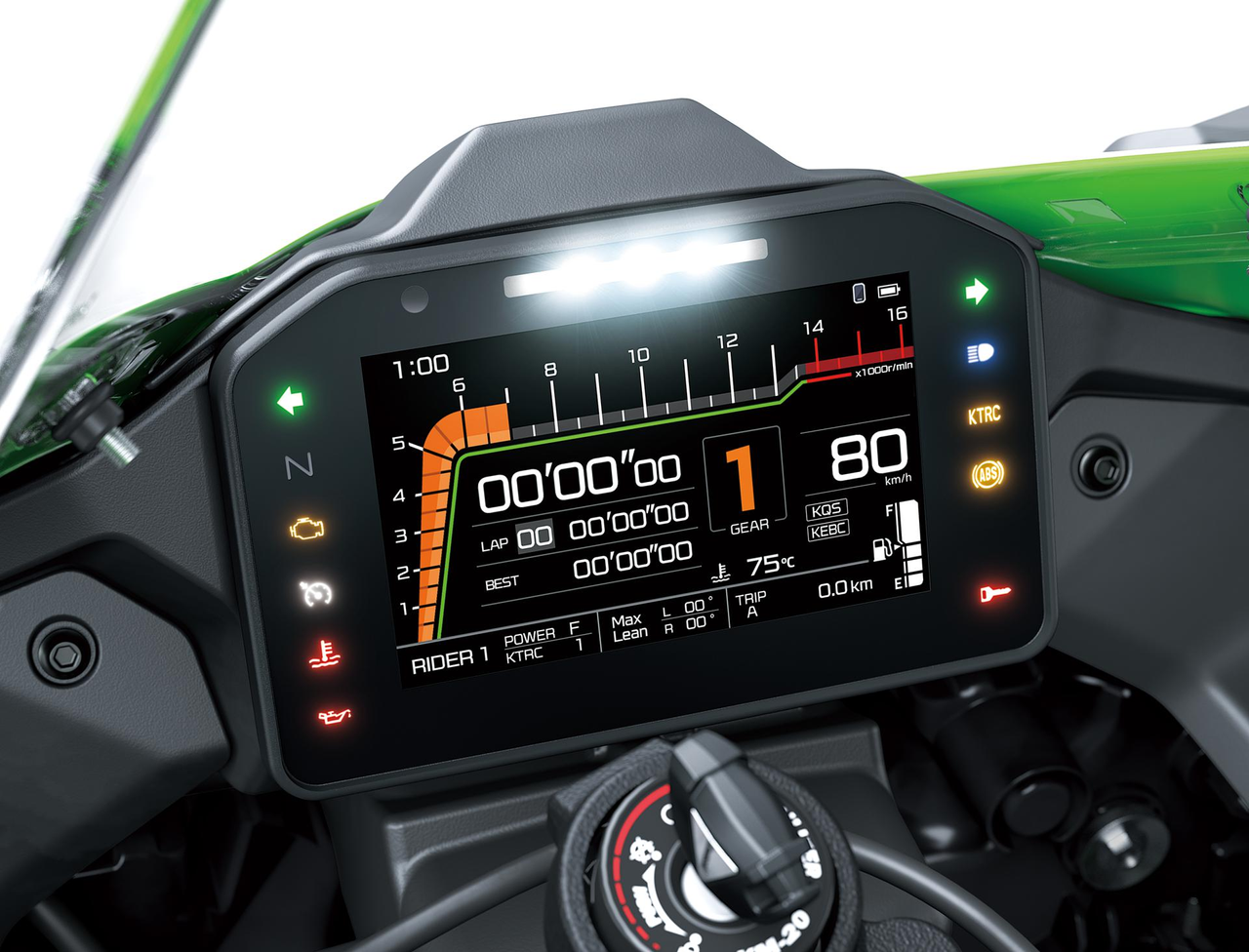

The highly sophisticated electronic management systems on the Ninja ZX-10RR facilitate rider control and allow riders to experience what it is like to ride a high-powered superbike at the limit on the track.
High-performance Pankl titanium connecting rods and lightweight Pankl pistons contribute to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s high-revving performance.

High-performance Pankl titanium connecting rods and lightweight Pankl pistons contribute to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s high-revving performance.
A prime example of form following function, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s latest bodywork was developed with aerodynamic performance as a top priority. The redesigned front cowl features large winglets that significantly increase downforce at high speeds. Combined with updated chassis geometry, the new aerodynamic package enhances high-speed control, cornering performance, and overall circuit potential.

A prime example of form following function, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s latest bodywork was developed with aerodynamic performance as a top priority. The redesigned front cowl features large winglets that significantly increase downforce at high speeds. Combined with updated chassis geometry, the new aerodynamic package enhances high-speed control, cornering performance, and overall circuit potential.
With an engine and chassis designed for chasing lap times on the track, the Ninja ZX-10RR offers a high level of circuit riding potential. To ensure it continues its race-winning ways, Kawasaki engineers fine-tuned the chassis geometry to fully capitalise on the enhanced aerodynamics.

With an engine and chassis designed for chasing lap times on the track, the Ninja ZX-10RR offers a high level of circuit riding potential. To ensure it continues its race-winning ways, Kawasaki engineers fine-tuned the chassis geometry to fully capitalise on the enhanced aerodynamics.
Powered by Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modelling program and enhanced with input from a Bosch IMU, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s cutting-edge electronics enhance the fun of piloting a high-performance supersport machine. Features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, and TFT instrumentation with turn-by-turn navigation capability add convenience and entertainment value, increasing street-riding enjoyment.

Powered by Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modelling program and enhanced with input from a Bosch IMU, the Ninja ZX-10RR’s cutting-edge electronics enhance the fun of piloting a high-performance supersport machine. Features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, and TFT instrumentation with turn-by-turn navigation capability add convenience and entertainment value, increasing street-riding enjoyment.
Dual high-spec Brembo M50 monobloc calipers gripping large Ø 330 mm discs, specially prepared radial-pump master cylinder and race-quality steel-braided lines deliver next-level braking performance.

Dual high-spec Brembo M50 monobloc calipers gripping large Ø 330 mm discs, specially prepared radial-pump master cylinder and race-quality steel-braided lines deliver next-level braking performance.
Adding to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s highly acclaimed control, cornering performance, and light handling, updates to the chassis geometry—tuned to match the effect of the new winglets—contribute to improved rear-wheel traction and enhanced secondary cornering force, which facilitates steering the bike from the rear when track riding.

Adding to the Ninja ZX-10RR’s highly acclaimed control, cornering performance, and light handling, updates to the chassis geometry—tuned to match the effect of the new winglets—contribute to improved rear-wheel traction and enhanced secondary cornering force, which facilitates steering the bike from the rear when track riding.
Circuit-focused settings for the WorldSBK-developed BFF (Balance Free Front Fork) and BFRC lite (Balance Free Rear Cushion) shock facilitate front-rear weight transfer and contribute to light handling.

Circuit-focused settings for the WorldSBK-developed BFF (Balance Free Front Fork) and BFRC lite (Balance Free Rear Cushion) shock facilitate front-rear weight transfer and contribute to light handling.
For riders who enjoy street riding, features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, smartphone connectivity, and full-colour TFT instrumentation with a gimbal-style lean angle display and turn-by-turn navigation* offer even greater satisfaction.
*Navigation functions will be available only to users who have a licence.
**Feature availability varies by market.

For riders who enjoy street riding, features like integrated Riding Modes, Electronic Cruise Control, smartphone connectivity, and full-colour TFT instrumentation with a gimbal-style lean angle display and turn-by-turn navigation* offer even greater satisfaction.
*Navigation functions will be available only to users who have a licence.
**Feature availability varies by market.
Handlebar and footpeg positions contribute to an aggressive, circuit-focused riding position that also helps riders minimise drag when tucked behind the windshield going down the straight.

Handlebar and footpeg positions contribute to an aggressive, circuit-focused riding position that also helps riders minimise drag when tucked behind the windshield going down the straight.
The Ninja ZX-10RR’s engine balances stunning power with manageability, offering linear power delivery right to its heady peak power. For maximum track-riding efficiency, great care was taken to ensure ideal engine manageability during all parts of the corner: getting off the throttle in corner entry, getting back on the throttle mid-corner, opening the throttle on corner exit. The new engine maintains the high performance of its predecessor while offering improved emissions.

The Ninja ZX-10RR’s engine balances stunning power with manageability, offering linear power delivery right to its heady peak power. For maximum track-riding efficiency, great care was taken to ensure ideal engine manageability during all parts of the corner: getting off the throttle in corner entry, getting back on the throttle mid-corner, opening the throttle on corner exit. The new engine maintains the high performance of its predecessor while offering improved emissions.
Compact projector/reflector hybrid headlights, repositioned Ram Air intake and prominent new winglets give the Ninja ZX-10RR its new “face,” enhancing the strong Ninja family image. All-new sharp, aggressive bodywork creates a dynamic image that completes the next-generation Ninja styling.

Compact projector/reflector hybrid headlights, repositioned Ram Air intake and prominent new winglets give the Ninja ZX-10RR its new “face,” enhancing the strong Ninja family image. All-new sharp, aggressive bodywork creates a dynamic image that completes the next-generation Ninja styling.
The winglets extending to either side not only highlight the machine’s advanced aerodynamic performance, but also effectively generate downforce that increases front-end feel for greater cornering confidence.

The winglets extending to either side not only highlight the machine’s advanced aerodynamic performance, but also effectively generate downforce that increases front-end feel for greater cornering confidence.
The highly sophisticated electronic management systems on the Ninja ZX-10RR facilitate rider control and allow riders to experience what it is like to ride a high-powered superbike at the limit on the track.

The highly sophisticated electronic management systems on the Ninja ZX-10RR facilitate rider control and allow riders to experience what it is like to ride a high-powered superbike at the limit on the track.
KCMF (Kawasaki Cornering Management Function) monitors engine and chassis parameters throughout the corner.

KCMF monitors engine and chassis parameters throughout the corner from entry, through the apex, to corner exit modulating brake force and engine power to facilitate smooth transition from acceleration to braking and back again, and to assist riders in tracing their intended line through the corner. KCMF oversees the following systems (where available): KTRC (including traction, wheelie and sliding control), KIBS (including pitching control), Kawasaki Engine Brake Control
Combined with Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modelling program, input from the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) enables even more precise chassis orientation awareness, the key to bringing Kawasaki’s electronics to the next level.

IMU means Enhanced Chassis Orientation Awareness. The strength of Kawasaki's cutting-edge electronics has always been the highly sophisticated programming that, using minimal hardware, gives the ECU an accurate real-time picture of what the chassis is doing. Kawasaki's proprietary dynamic modelling program makes skillful use of the magic formula tyre model as it examines changes in multiple parameters, enabling it to take into account changing road and tyre conditions. The addition of an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) enables inertia along 6 DOF (degrees of freedom) to be monitored. Acceleration along longitudinal, transverse and vertical axes, plus roll rate and pitch rate are measured. The yaw rate is calculated by the ECU. This additional feedback contributes to an even clearer real-time picture of chassis orientation, enabling even more precise management for control at the limit. With the addition of the IMU and the latest evolution of Kawasaki's advanced modelling software, Kawasaki's electronic engine and chassis management technology takes the step to the next level changing from setting-type and reaction-type systems to feedback-type systems to deliver even greater levels of riding excitement.
S-KTRC (Sport-Kawasaki TRaction Control) is a racing technology-based predictive traction control system designed to help riders push harder on the racetrack by maximising acceleration.

S-KTRC, Kawasaki's original predictive traction control, uses the same base technology as Kawasaki’s works machines. Designed to maximise acceleration, it allows riding at the edge of traction on the track. This technology continually controls the rear wheel slip that occurs when power is applied, ensuring optimal acceleration. In general, maximum forward drive requires a certain amount of slip. To ensure the most effective transfer of power to the tarmac, S-KTRC monitors the slip ratio in real time, and governs engine power delivery to optimise rear wheel traction.
S-KTRC monitors a number of parameters, including front and rear wheel speed (slip), engine rpm, throttle position and acceleration. Conditions are confirmed every 5 milliseconds, at which time the system looks at each of the parameters as well has how much they are changing (i.e. their rate of change). This unique Kawasaki method makes it possible to make interpolations and precisely calibrate engine output to suit traction conditions. By acting before slippage exceeds the limits of traction, drops in power can be minimised, resulting in ultra-smooth operation.
Because the sophisticated software bases its dynamic analysis on the chassis’ orientation relative to the track surface (rather than relative to a horizontal plane), it is able to take into account corner camber, gradient, etc, and adapt accordingly. It also automatically adjusts for tyre wear, different tyre profiles, high-grip tyres, and numerous other factors that setting-type systems treat as fixed parameters. Models equipped with IMU incorporate chassis-orientation feedback to offer even more precise management.
KLCM (Kawasaki Launch Control Mode) optimises acceleration from a stop by electronically managing engine output to prevent wheelspin.

Designed to assist riders by optimising acceleration from a stop, KLCM electronically manages engine output to prevent wheelspin when moving off. Riders can choose from three modes, each offering a progressively greater level of intrusion. Each mode allows the rider to leave from a stop with the throttle held wide open. With the clutch lever pulled in and the system activated, engine speed is limited to a determined speed while the rider holds the throttle open. Once the rider releases the clutch lever to engage the clutch, engine speed is allowed to increase, but power is regulated to prevent wheelspin and help keep the front wheel on the ground. (In Mode 1, the least intrusive, the front wheel may lift a little.) The system disengages automatically at 150 km/h or when the rider shifts into 3rd gear.
KEBC (Kawasaki Engine Brake Control) allows riders to select their preferred amount of engine braking.
Engine braking can be used advantageously to help a bike decelerate, but not all riders prefer strong engine braking. With KEBC, riders are able to select the amount of engine braking they prefer. When KEBC is activated, the engine braking effect is reduced, providing less interference when riding on the circuit.

Designed to help riders maximise their acceleration on the circuit by enabling clutchless upshifts with the throttle fully open, KQS detects that the shift lever has been actuated and sends a signal to the ECU to cut ignition so that the next gear can be engaged without having to use the clutch. On models that offer clutchless downshifts, during deceleration the system automatically controls engine speed so that the next lower gear can be selected without operating the clutch.
Electronic Throttle Valves allow the ECU to deliver the ideal amount of fuel and air to the engine.

Kawasaki's fully electronic throttle actuation system enables the ECU to control the volume of both the fuel (via fuel injectors) and the air (via throttle valves) delivered to the engine. Ideal fuel injection and throttle valve position results in smooth, natural engine response and the ideal engine output. The system also makes a significant contribution to reduced emissions. Electronic throttle valves also enable more precise control of electronic engine management systems like S-KTRC and KTRC, and allow the implementation of electronic systems like KLCM, Kawasaki Engine Brake Control, and Electronic Cruise Control.
KIBS (Kawasaki Intelligent anti-lock Brake System) is a high-precision brake system designed specifically for supersport models, offering highly efficient braking while maintaining natural feel.

Kawasaki developed KIBS to take into account the particular handling characteristics of supersport motorcycles, ensuring highly efficient braking with minimal intrusion during hard sport riding. It is the first mass-production brake system to link the ABS ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and engine ECU. In addition front and rear wheel speed, KIBS monitors front brake caliper hydraulic pressure, throttle position, engine speed, clutch actuation and gear position. This diverse information is analysed to determine the ideal front brake hydraulic pressure. Through precise control, the large drops in hydraulic pressure seen on standard ABS systems can be avoided. Additionally, the tendency on supersport models for the rear wheel to lift under heavy braking can be suppressed and rear brake controllability can be maintained when downshifting.
Horizontal Back-link Rear Suspension arranges its shock unit horizontally, greatly contributing to efficient use of space and mass centralisation.

Compared to Kawasaki's traditional Uni-Trak rear suspension, which mounts the shock unit vertically, with Horizontal Back-link rear suspension, the shock unit is almost horizontal. Kawasaki's original suspension arrangement locates the shock unit very close to the bike's centre of gravity, greatly contributing to mass centralisation. And because there is no linkage or shock unit protruding beneath the swingarm, this frees up space for a larger exhaust pre-chamber (an exhaust expansion chamber situated just upstream of the silencer). With a larger pre-chamber, silencer volume can be reduced, and heavy exhaust components can be concentrated closer to the centre of the bike, further contributing to mass centralisation. The result is greatly improved handling. Another benefit is that the shock unit is placed far away from exhaust heat. Because it is more difficult for heat from the exhaust system to adversely affect suspension oil and gas pressure, suspension performance is more stable. Horizontal Back-link rear suspension offers numerous secondary benefits like this.
Smartphone connectivity contributes to an enhanced motorcycling experience by enabling riders to connect to their motorcycle wirelessly.

Clever technology enables riders to connect to their motorcycle wirelessly. Using the smartphone application RIDEOLOGY THE APP a number of instrument functions can be accessed, contributing to an enhanced motorcycling experience. Vehicle information (such as the odometer, fuel gauge, maintenance schedule, etc) can be viewed on the smartphone. Riding logs (varies by model, but may include GPS route, gear position, rpm, and other information) can be viewed on the smartphone. When connected, telephone (call, mail) notices are displayed on the instrument panel. Riders can also make changes to their motorcycle instrument display settings (preferred units, clock and date setting, etc) via the smartphone. And on certain models, it is even possible to check and adjust vehicle settings (such as Rider Mode, electronic rider support features, and payload settings) using the smartphone.
Power Mode selection allows engine power delivery to be changed to suit the riding situation.
Models equipped with multiple Power Modes offer riders an easily selectable choice of engine power delivery to suit riding conditions or preference. In addition to Full Power mode, one (Low) or two (Middle, Low) alternate mode(s) in which maximum power is limited and throttle response is milder are provided.
Electronic Cruise Control allows vehicle speed to be fixed. Rider support technology that helps reduce rider fatigue on long trips and contributes to increased touring comfort.

Electronic Cruise Control allows a desired speed (engine rpm) to be maintained with the simple press of a button. Once activated, the rider does not have to constantly apply the throttle. This reduces stress on the right hand when travelling long distances, enabling relaxed cruising and contributing to a high level of riding comfort.
The Economical Riding Indicator is a mark appearing on the instrument panel to indicate favourable fuel consumption, encouraging fuel efficient riding.

Using high-precision electronic control for engine management, Kawasaki models can achieve a high level of fuel efficiency. However, fuel consumption is greatly affected by throttle use, gear selection, and other elements under the rider's control. The Economical Riding Indicator is a function that indicates when current riding conditions are consuming a low amount of fuel. The system continuously monitors fuel consumption, regardless of vehicle speed, engine speed, throttle position and other riding conditions. When fuel consumption is low for a given speed (i.e. fuel efficiency is high), an "ECO" mark appears on the instrument panel's LCD screen. By riding so that the "ECO" mark remains on, fuel consumption can be reduced. While effective vehicle speed and engine speed may vary by model, paying attention to conditions that cause the "ECO" mark to appear can help riders improve their fuel efficiency – a handy way to increase cruising range. Further, keeping fuel consumption low also helps minimise negative impact on the environment.
ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) ensures stable braking performance by preventing wheel lock during braking.

Sudden over-application of the brakes, or braking on low-grip surfaces (surfaces with a low coefficient of friction) such as wet asphalt or manhole covers may cause a motorcycle's wheel(s) to lock up and slip. ABS was developed to prevent such incidents. Kawasaki ABS systems are controlled by high precision and highly reliable programming formulated based on thorough testing of numerous riding situations. By ensuring stable braking performance, they offer rider reassurance that contributes to greater riding enjoyment. And to meet the special requirements of certain riders, specialised ABS systems are also available. For example, KIBS (Kawasaki Intelligent anti-lock Brake System) is a high-precision brake system designed specifically for supersport models, enabling sport riding to be enjoyed by a wider range of riders. And by linking the front and rear brakes, K-ACT (Kawasaki Advanced Coactive-braking Technology) ABS provides the confidence to enjoy touring on heavyweight models. Kawasaki is continually working on the development of other advanced ABS systems.
KCMF (Kawasaki Cornering Management Function) monitors engine and chassis parameters throughout the corner.

KCMF monitors engine and chassis parameters throughout the corner from entry, through the apex, to corner exit modulating brake force and engine power to facilitate smooth transition from acceleration to braking and back again, and to assist riders in tracing their intended line through the corner. KCMF oversees the following systems (where available): KTRC (including traction, wheelie and sliding control), KIBS (including pitching control), Kawasaki Engine Brake Control
Combined with Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modelling program, input from the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) enables even more precise chassis orientation awareness, the key to bringing Kawasaki’s electronics to the next level.

IMU means Enhanced Chassis Orientation Awareness. The strength of Kawasaki's cutting-edge electronics has always been the highly sophisticated programming that, using minimal hardware, gives the ECU an accurate real-time picture of what the chassis is doing. Kawasaki's proprietary dynamic modelling program makes skillful use of the magic formula tyre model as it examines changes in multiple parameters, enabling it to take into account changing road and tyre conditions. The addition of an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) enables inertia along 6 DOF (degrees of freedom) to be monitored. Acceleration along longitudinal, transverse and vertical axes, plus roll rate and pitch rate are measured. The yaw rate is calculated by the ECU. This additional feedback contributes to an even clearer real-time picture of chassis orientation, enabling even more precise management for control at the limit. With the addition of the IMU and the latest evolution of Kawasaki's advanced modelling software, Kawasaki's electronic engine and chassis management technology takes the step to the next level changing from setting-type and reaction-type systems to feedback-type systems to deliver even greater levels of riding excitement.
S-KTRC (Sport-Kawasaki TRaction Control) is a racing technology-based predictive traction control system designed to help riders push harder on the racetrack by maximising acceleration.

S-KTRC, Kawasaki's original predictive traction control, uses the same base technology as Kawasaki’s works machines. Designed to maximise acceleration, it allows riding at the edge of traction on the track. This technology continually controls the rear wheel slip that occurs when power is applied, ensuring optimal acceleration. In general, maximum forward drive requires a certain amount of slip. To ensure the most effective transfer of power to the tarmac, S-KTRC monitors the slip ratio in real time, and governs engine power delivery to optimise rear wheel traction.
S-KTRC monitors a number of parameters, including front and rear wheel speed (slip), engine rpm, throttle position and acceleration. Conditions are confirmed every 5 milliseconds, at which time the system looks at each of the parameters as well has how much they are changing (i.e. their rate of change). This unique Kawasaki method makes it possible to make interpolations and precisely calibrate engine output to suit traction conditions. By acting before slippage exceeds the limits of traction, drops in power can be minimised, resulting in ultra-smooth operation.
Because the sophisticated software bases its dynamic analysis on the chassis’ orientation relative to the track surface (rather than relative to a horizontal plane), it is able to take into account corner camber, gradient, etc, and adapt accordingly. It also automatically adjusts for tyre wear, different tyre profiles, high-grip tyres, and numerous other factors that setting-type systems treat as fixed parameters. Models equipped with IMU incorporate chassis-orientation feedback to offer even more precise management.
KLCM (Kawasaki Launch Control Mode) optimises acceleration from a stop by electronically managing engine output to prevent wheelspin.

Designed to assist riders by optimising acceleration from a stop, KLCM electronically manages engine output to prevent wheelspin when moving off. Riders can choose from three modes, each offering a progressively greater level of intrusion. Each mode allows the rider to leave from a stop with the throttle held wide open. With the clutch lever pulled in and the system activated, engine speed is limited to a determined speed while the rider holds the throttle open. Once the rider releases the clutch lever to engage the clutch, engine speed is allowed to increase, but power is regulated to prevent wheelspin and help keep the front wheel on the ground. (In Mode 1, the least intrusive, the front wheel may lift a little.) The system disengages automatically at 150 km/h or when the rider shifts into 3rd gear.
KEBC (Kawasaki Engine Brake Control) allows riders to select their preferred amount of engine braking.
Engine braking can be used advantageously to help a bike decelerate, but not all riders prefer strong engine braking. With KEBC, riders are able to select the amount of engine braking they prefer. When KEBC is activated, the engine braking effect is reduced, providing less interference when riding on the circuit.

Designed to help riders maximise their acceleration on the circuit by enabling clutchless upshifts with the throttle fully open, KQS detects that the shift lever has been actuated and sends a signal to the ECU to cut ignition so that the next gear can be engaged without having to use the clutch. On models that offer clutchless downshifts, during deceleration the system automatically controls engine speed so that the next lower gear can be selected without operating the clutch.
Electronic Throttle Valves allow the ECU to deliver the ideal amount of fuel and air to the engine.

Kawasaki's fully electronic throttle actuation system enables the ECU to control the volume of both the fuel (via fuel injectors) and the air (via throttle valves) delivered to the engine. Ideal fuel injection and throttle valve position results in smooth, natural engine response and the ideal engine output. The system also makes a significant contribution to reduced emissions. Electronic throttle valves also enable more precise control of electronic engine management systems like S-KTRC and KTRC, and allow the implementation of electronic systems like KLCM, Kawasaki Engine Brake Control, and Electronic Cruise Control.
KIBS (Kawasaki Intelligent anti-lock Brake System) is a high-precision brake system designed specifically for supersport models, offering highly efficient braking while maintaining natural feel.

Kawasaki developed KIBS to take into account the particular handling characteristics of supersport motorcycles, ensuring highly efficient braking with minimal intrusion during hard sport riding. It is the first mass-production brake system to link the ABS ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and engine ECU. In addition front and rear wheel speed, KIBS monitors front brake caliper hydraulic pressure, throttle position, engine speed, clutch actuation and gear position. This diverse information is analysed to determine the ideal front brake hydraulic pressure. Through precise control, the large drops in hydraulic pressure seen on standard ABS systems can be avoided. Additionally, the tendency on supersport models for the rear wheel to lift under heavy braking can be suppressed and rear brake controllability can be maintained when downshifting.
Horizontal Back-link Rear Suspension arranges its shock unit horizontally, greatly contributing to efficient use of space and mass centralisation.

Compared to Kawasaki's traditional Uni-Trak rear suspension, which mounts the shock unit vertically, with Horizontal Back-link rear suspension, the shock unit is almost horizontal. Kawasaki's original suspension arrangement locates the shock unit very close to the bike's centre of gravity, greatly contributing to mass centralisation. And because there is no linkage or shock unit protruding beneath the swingarm, this frees up space for a larger exhaust pre-chamber (an exhaust expansion chamber situated just upstream of the silencer). With a larger pre-chamber, silencer volume can be reduced, and heavy exhaust components can be concentrated closer to the centre of the bike, further contributing to mass centralisation. The result is greatly improved handling. Another benefit is that the shock unit is placed far away from exhaust heat. Because it is more difficult for heat from the exhaust system to adversely affect suspension oil and gas pressure, suspension performance is more stable. Horizontal Back-link rear suspension offers numerous secondary benefits like this.
Smartphone connectivity contributes to an enhanced motorcycling experience by enabling riders to connect to their motorcycle wirelessly.

Clever technology enables riders to connect to their motorcycle wirelessly. Using the smartphone application RIDEOLOGY THE APP a number of instrument functions can be accessed, contributing to an enhanced motorcycling experience. Vehicle information (such as the odometer, fuel gauge, maintenance schedule, etc) can be viewed on the smartphone. Riding logs (varies by model, but may include GPS route, gear position, rpm, and other information) can be viewed on the smartphone. When connected, telephone (call, mail) notices are displayed on the instrument panel. Riders can also make changes to their motorcycle instrument display settings (preferred units, clock and date setting, etc) via the smartphone. And on certain models, it is even possible to check and adjust vehicle settings (such as Rider Mode, electronic rider support features, and payload settings) using the smartphone.
Power Mode selection allows engine power delivery to be changed to suit the riding situation.
Models equipped with multiple Power Modes offer riders an easily selectable choice of engine power delivery to suit riding conditions or preference. In addition to Full Power mode, one (Low) or two (Middle, Low) alternate mode(s) in which maximum power is limited and throttle response is milder are provided.
Electronic Cruise Control allows vehicle speed to be fixed. Rider support technology that helps reduce rider fatigue on long trips and contributes to increased touring comfort.

Electronic Cruise Control allows a desired speed (engine rpm) to be maintained with the simple press of a button. Once activated, the rider does not have to constantly apply the throttle. This reduces stress on the right hand when travelling long distances, enabling relaxed cruising and contributing to a high level of riding comfort.
The Economical Riding Indicator is a mark appearing on the instrument panel to indicate favourable fuel consumption, encouraging fuel efficient riding.

Using high-precision electronic control for engine management, Kawasaki models can achieve a high level of fuel efficiency. However, fuel consumption is greatly affected by throttle use, gear selection, and other elements under the rider's control. The Economical Riding Indicator is a function that indicates when current riding conditions are consuming a low amount of fuel. The system continuously monitors fuel consumption, regardless of vehicle speed, engine speed, throttle position and other riding conditions. When fuel consumption is low for a given speed (i.e. fuel efficiency is high), an "ECO" mark appears on the instrument panel's LCD screen. By riding so that the "ECO" mark remains on, fuel consumption can be reduced. While effective vehicle speed and engine speed may vary by model, paying attention to conditions that cause the "ECO" mark to appear can help riders improve their fuel efficiency – a handy way to increase cruising range. Further, keeping fuel consumption low also helps minimise negative impact on the environment.
ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) ensures stable braking performance by preventing wheel lock during braking.

Sudden over-application of the brakes, or braking on low-grip surfaces (surfaces with a low coefficient of friction) such as wet asphalt or manhole covers may cause a motorcycle's wheel(s) to lock up and slip. ABS was developed to prevent such incidents. Kawasaki ABS systems are controlled by high precision and highly reliable programming formulated based on thorough testing of numerous riding situations. By ensuring stable braking performance, they offer rider reassurance that contributes to greater riding enjoyment. And to meet the special requirements of certain riders, specialised ABS systems are also available. For example, KIBS (Kawasaki Intelligent anti-lock Brake System) is a high-precision brake system designed specifically for supersport models, enabling sport riding to be enjoyed by a wider range of riders. And by linking the front and rear brakes, K-ACT (Kawasaki Advanced Coactive-braking Technology) ABS provides the confidence to enjoy touring on heavyweight models. Kawasaki is continually working on the development of other advanced ABS systems.
| Engine type | Liquid-cooled, 4-stroke, in-line four |
|---|---|
| Compression ratio | 13.0:1 |
| Valve system | DOHC, 16 valves |
| Bore x stroke | 76.0 x 55.0 mm |
| Displacement | 998 cm³ |
| Fuel system | Fuel injection with dual injection: 47 mm x 4 |
| Lubrication | Forced lubrication, wet sump with oil cooler |
| Starting system | Electric |
| Ignition system | Digital |
| Maximum power | 145.0 kW {197 PS} / 13,200 rpm |
|---|---|
| Maximum power with RAM Air | 152.3 kW {207 PS} / 13,200 rpm |
| Maximum torque | 110.0 N•m {11.2 kgf•m} / 11,400 rpm |
| CO2 emission | 147 g/km |
| Fuel consumption | 6.3 l/100km |
| Frame type | Twin spar, cast aluminium |
|---|---|
| Trail | 105 mm |
| Wheel travel front | 120 mm |
| Wheel travel rear | 107 mm |
| Tyre, front | 120/70 ZR17 M/C (58W) |
| Tyre, rear | 190/55 ZR17 M/C (75W) |
| L x W x H | 2,085 x 750 x 1,180 mm |
| Steering angle L/R | 27° / 27° |
| Wheel base | 1,450 mm |
| Ground clearance | 130 mm |
| Fuel capacity | 17.0 litres |
| Seat height | 825 mm |
| Curb mass* | 207 kg |
| | *Curb mass includes all necessary materials and fluids to operate correctly, full tank of fuel (more than 90 percent capacity) and tool kit (if supplied). |
| Estimated dry weight** | 190 kg |
| | **Estimated Dry weight does not include all necessary materials and fluids to operate correctly, full tank of fuel (more than 90 percent capacity) and tool kit (if supplied). |
| Front brake type | Dual semi-floating Brembo discs |
|---|---|
| Front brake diameter | Ø 330 mm |
| Front brake caliper type | Brembo radial-mount, M50 monobloc, opposed 4-piston |
| Rear brake type | Single disc |
| Rear brake diameter | Ø 220 mm |
| Rear brake caliper type | Single-bore pin-slide |
| Front suspension type | Inverted Balance Free fork with external compression chamber, compression and rebound damping, spring preload adjustability, and top-out springs |
| Front suspension diameter | Ø 43 mm |
| Rear suspension type | Horizontal Back-link, BFRC lite gas-charged shock with piggyback reservoir, compression and rebound damping, spring preload adjustability, and top-out spring |
Inpage Navigation Section: Accessories

Tyre shaped keyring with removable tag
Help keep your hands warm on the road with a grip heater system ergonomically designed to minimize added bulk to the grip.
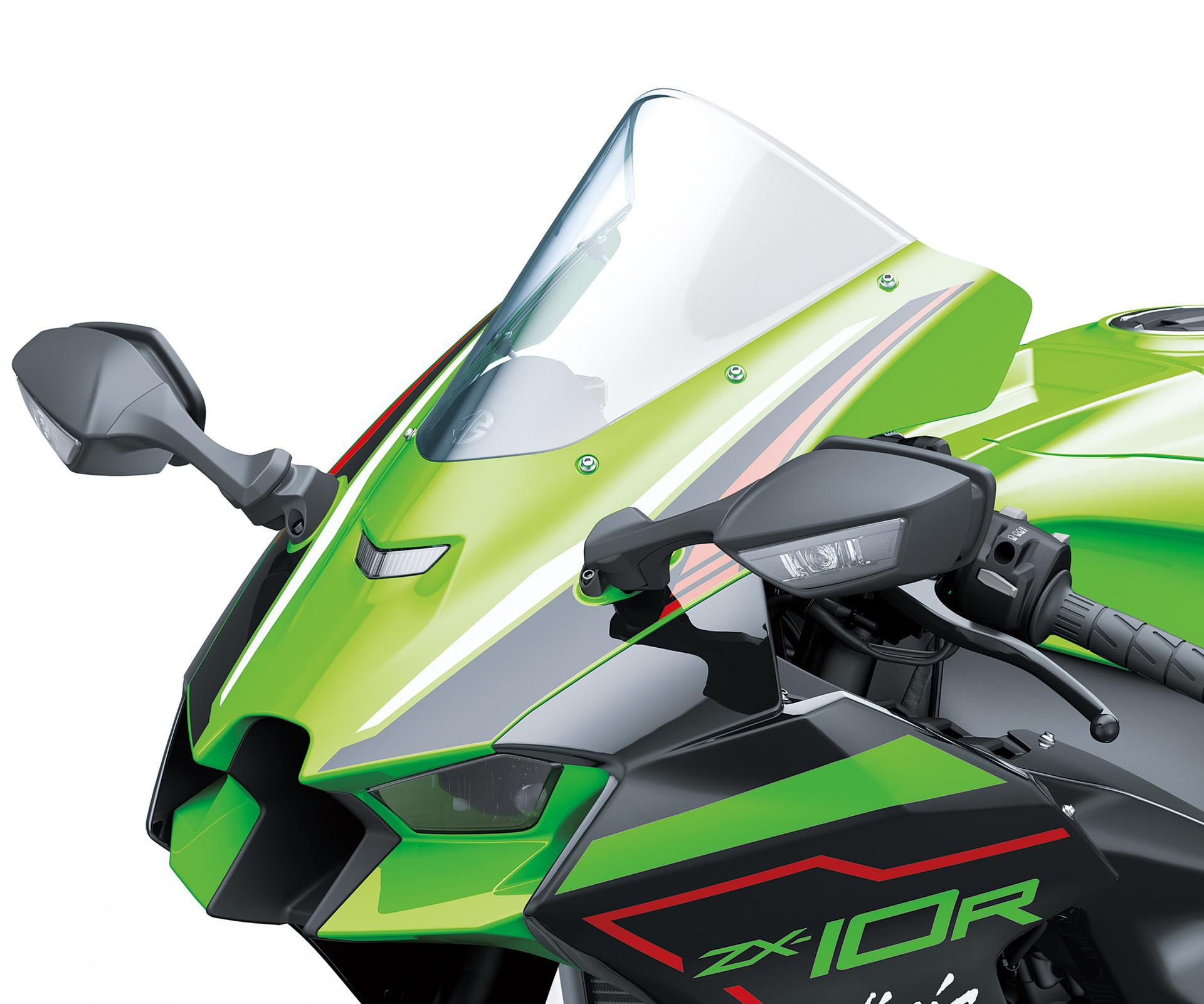

This tinted, race style smoke windscreen is designed to reduce wind pressure and improve aerodynamics. Homologated with bike type approval.
Tyre warmer set "Advanced" Fitted with a high-precision thermo switch, this instrument informs you when the temperature (80°C) is reached and will keep it within a range of +- 2°C.
Heating part is made of a carbon resistor covered with thermo conductive silicon. Material in contact with the tyre is anti-adherent, anti-cut and anti-abrasion. External surface is washable.
Made from strong Anti-tear Honeycomb ripstop fabric. Heat resistance till 120 degrees Celcius. Subtle branding.
100% Polyester. With multi usable (back)packing string bag.
Fits:
Whether you want to park your bike in a pitbox or in your garage, let your precious machine rest in style on this Kawasaki Garage Mat. The mat meets new FIM environmental codes and offers a high level of absorption and dust-control features.
